Do Bees Have A Central Nervous System?
Yes, bees have a central nervous system that is typical of insects.
The central nervous system in bees comprises a brain, linked to a central nerve cord which runs through the body of the bee (along the thorax and abdomen), with paired swellings known as ganglia, occurring at intervals along it, and lateral nerves spread out from these.
What does the central nervous system in bees do?
Sensory information is received and processed by the brain and ganglia of the bee. This in turn stimulates a response in the form of a physiological action or behavioral activity.
The parts and functions of the honey bee central nervous system
Because such a large amount of information and research has been undertaken specifically on the honey bee, (Apis), we'll focus on the central nervous system of this species.
Below is a diagram of the nervous system of the honey bee from The Anatomy Of The Honey Bee by R. E. Snodgrass.
It shows the brain (Br) and 7 ganglia (Gng), 2 of which are situated in the the thorax, and 5 in the abdomen.
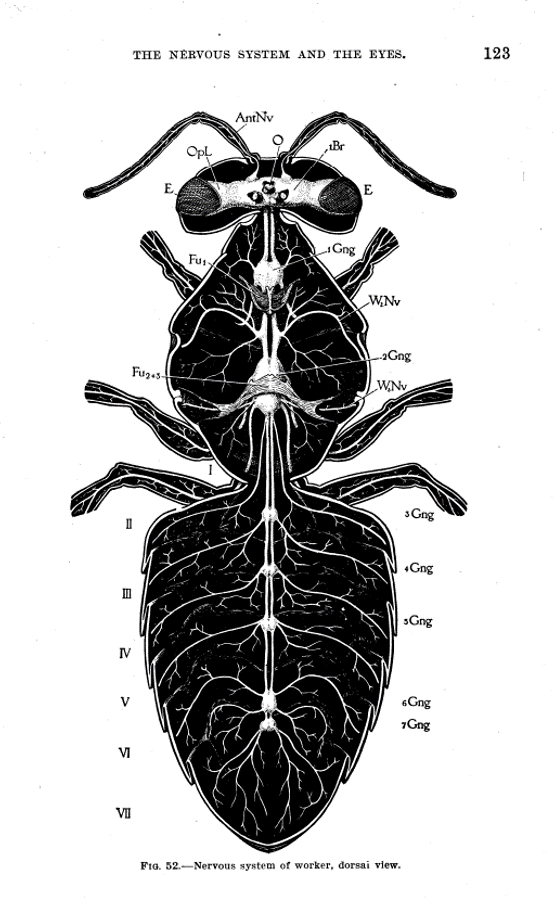
Key parts of the honey bee central nervous system.
The Brain
The brain itself features a number of structures, such as optic lobes, mushroom bodies, antennal lobes and neurons.
The different and various structures of the brain are associated with, for example, visual processing from information picked up by the eyes, motion sensitivity, olfactory learning, memory (see Are bees smart?).
Ganglia:
There are 7 ganglia running along the body of the bee. The ganglia contain the nerve cells which receive information from the sense organs, and stimulate other tissues.
The thoracic ganglia (i.e. the 2 ganglia located in the thorax) control the wings and legs.
Commissures:
Cords connecting the ganglia. The commissures and the nerve-trunks that branch to all parts of the body consist of fibers. These fibers are extensions of the nerve cells, and act like electric wires, conveying information to and from the nerve centers.
The parts of the central nervous system also co-ordinate in order to perform various functions, for example the waggle dance, which includes aspects of learning and behaviours associated with the brain, along with bodily movement of the wings and legs.
References
- Sen Sarma M, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Hong F, Zhong S, Robinson GE (2009) Transcriptomic Profiling of Central Nervous System Regions in Three Species of Honey Bee during Dance Communication Behavior. PLoS ONE 4(7): e6408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006408
- THE ANATOMY OF THE HONEY BEE.
BY
R. E. SNODGRASS, MAY 28, 1910.